Reduce High TTFB in WordPress — Expert Guide to Improve Server Response Time

TTFB (Time to First Byte) is the time it takes for a user’s browser to receive the first byte of response from your server. A high TTFB slows everything down — your page speed, Core Web Vitals, and even SEO rankings. In this in-depth guide, we’ll explain what TTFB is, why it matters, and how to fix it with proven, technical steps used by performance professionals.

What Is TTFB and Why It Matters
TTFB measures the delay between your browser’s request and your server’s first response. It includes three phases:
- DNS Lookup — resolving your domain to an IP address.
- Server Connection — establishing TCP/TLS connection.
- Waiting for the Server Response — generating the first byte of data.
A good TTFB is below 200 ms. Anything above 500 ms usually indicates a performance bottleneck such as slow hosting, inefficient PHP code, or lack of caching.
Why TTFB Is Crucial for WordPress Performance

TTFB directly impacts how quickly your website starts to render. The faster the first byte arrives, the sooner the browser can begin building and displaying the page. For WordPress, which relies heavily on PHP and database queries, TTFB can make or break perceived performance.
- UX Impact: Slow TTFB delays page rendering and frustrates visitors.
- SEO Impact: Google considers server response time as part of page experience signals.
- Server Efficiency: High TTFB means wasted CPU cycles and poor caching strategy.
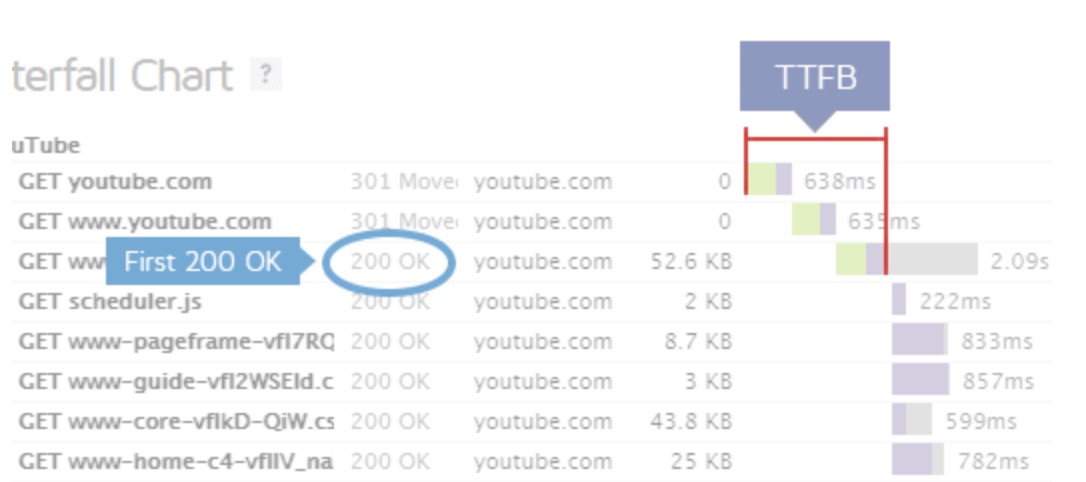
How to Measure TTFB Accurately
- Chrome DevTools: Open DevTools → Network tab → select the main document → check Waiting (TTFB) value.
- PageSpeed Insights: Look for “Reduce initial server response time” warning.
- WebPageTest or GTmetrix: Analyze TTFB across global test servers.
- Server-side monitoring: Tools like New Relic or Query Monitor show backend processing time per request.
Main Causes of High TTFB in WordPress
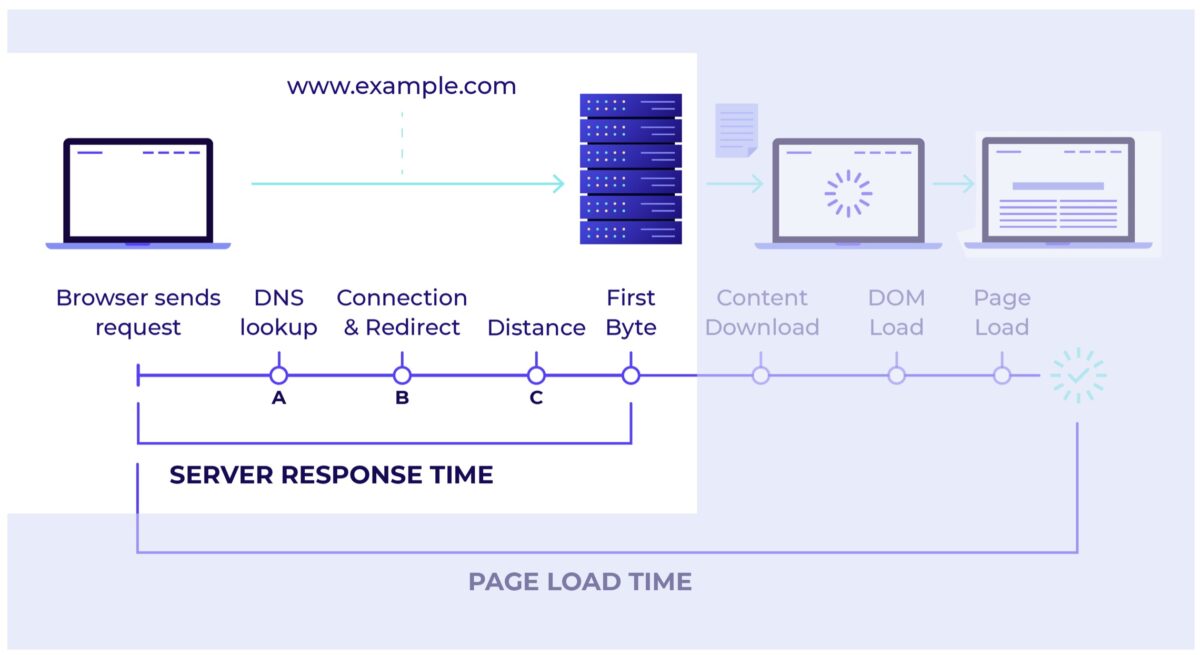
Main Causes of High TTFB in WordPress
- Slow or overloaded hosting — shared servers or poor hardware cause delayed response times.
- No page caching — WordPress regenerates every page via PHP and MySQL on each request.
- Heavy themes or plugins — excessive queries and hooks delay server output.
- Unoptimized database — bloated
wp_options, transients, or missing indexes. - No CDN or distant server location — physical latency between users and the server.
- Slow DNS or SSL handshake — poor DNS resolver or outdated TLS protocols.
- Old PHP version — PHP 5.x is 2–3× slower than PHP 8.2+.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Reduce High TTFB in WordPress
1. Use a Fast, Optimized Hosting Provider
Choose a host with LiteSpeed, NGINX, or a managed WordPress stack. Look for SSD/NVMe storage, HTTP/3 support, and low global latency. Avoid cheap shared hosting — it’s the #1 reason for TTFB above 500 ms.
2. Enable Full Page Caching
Install LiteSpeed Cache, WP Rocket, or WP Fastest Cache. These plugins serve static HTML instead of regenerating PHP pages on every visit. Check response headers for X-Cache: HIT.
3. Optimize Your Database
Clean the wp_options table, remove transients, spam, revisions, and unnecessary autoload data. You can follow our guide: Optimize wp_options Table.
4. Use a CDN (Content Delivery Network)
CDNs like Cloudflare or BunnyCDN cache your static assets at edge locations close to users, drastically lowering latency and reducing TTFB from distant regions.
5. Implement Object Cache (Redis / Memcached)
Object caching stores database query results in memory. It’s crucial for large sites or WooCommerce stores where repeated queries slow down PHP processing.
6. Upgrade PHP and Server Configuration
Always use PHP 8.1 or 8.2 with OPcache enabled. Set proper limits:
memory_limit = 512M, max_execution_time = 120. Use PHP-FPM for efficient worker pools.
7. Minimize External Requests
Disable or delay third-party APIs (analytics, chat, social scripts) that block the response. Defer non-critical JS and preload DNS for required domains.
8. Optimize DNS and TLS
Use fast resolvers like Cloudflare DNS or Google DNS. Ensure TLS 1.3 and HTTP/3 are enabled on your host.
9. Monitor and Benchmark Regularly
After changes, re-test TTFB using GTmetrix and WebPageTest from multiple regions. Aim for under 200 ms consistently.
Advanced TTFB Optimization Techniques
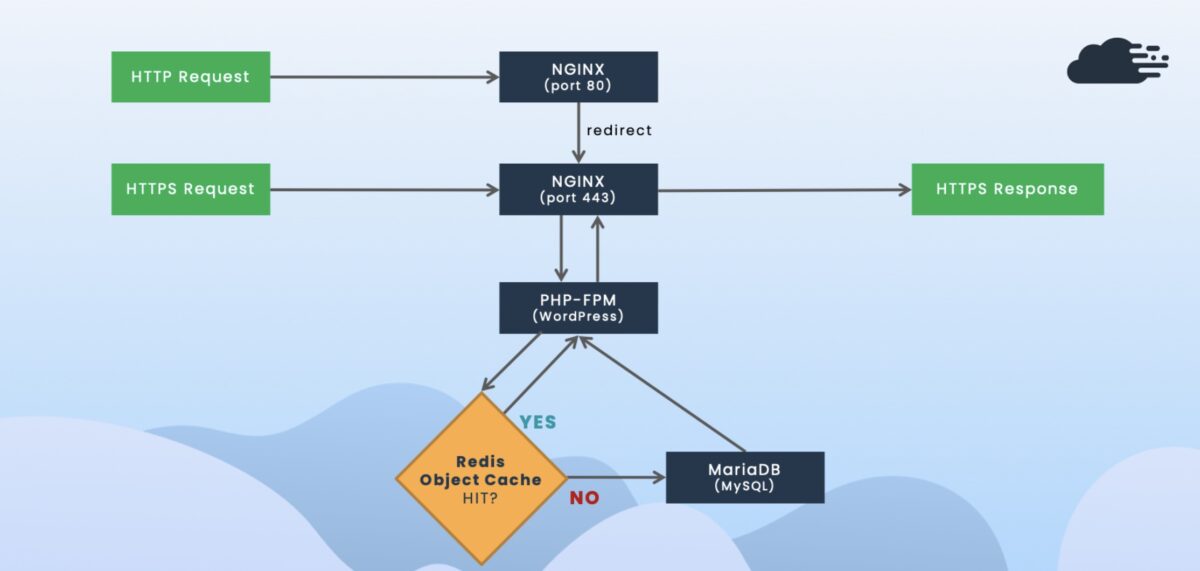
- Redis / Memcached: Caches object data and database queries in RAM.
- OPcache: Stores precompiled PHP bytecode, reducing CPU load.
- PHP-FPM Tuning: Adjust
pm.max_childrenandpm.max_requeststo match traffic volume. - HTTP/3 + QUIC: Enable on your CDN or server to cut latency.
- Edge Caching: Cache full pages at CDN edges (Cloudflare APO, Bunny Edge Rules).
- Server Hardware: Prefer NVMe SSD over HDD; low disk I/O equals faster response.
Pre-Launch TTFB Checklist
- TTFB under 200 ms globally (WebPageTest)
- Page caching enabled and verified (
X-Cache: HIT) - Redis or Memcached active
- CDN configured and edge cache above 90%
- Database optimized and cleaned
- PHP 8.1+ with OPcache enabled
- HTTP/3 + TLS 1.3 active
- No unnecessary redirects (301/302)
- Monitor with New Relic or UptimeRobot
FAQ: Common Questions About TTFB
Q: Does low TTFB guarantee a fast website?
A: Not necessarily. It’s a foundation — but large JS/CSS files and slow frontend rendering can still make a site slow.
Q: How soon can I see improvement after optimizing TTFB?
A: In most cases, within hours. Major code or hosting changes may take longer to reflect in global CDN caches.
Q: Which hosting has the best TTFB?
A: Managed WordPress hosts with LiteSpeed or NGINX stacks — like Cloudways, Rocket.net, or Kinsta — consistently deliver <200 ms TTFB.
Q: Does TTFB affect SEO rankings?
A: Indirectly yes — it impacts Core Web Vitals and crawl efficiency, both of which affect search performance.
Final Thoughts
Optimizing TTFB is one of the most effective ways to improve both server efficiency and user experience. By combining fast hosting, aggressive caching, and clean code, you can easily achieve TTFB below 200 ms and unlock top Core Web Vitals scores.
Need help analyzing your server or database bottlenecks? Request a free performance audit from SpeedWP Pro — we’ll test your site, inspect logs, and provide actionable fixes tailored for your WordPress setup.
