Оптимизация базы данных WordPress: приемы работы с MySQL, выходящие за рамки плагинов.
Почему оптимизация базы данных имеет значение
A slow WordPress website is not always caused by large images or weak hosting. Very often, the real bottleneck hides inside the MySQL database. As WordPress grows, it accumulates unnecessary data such as old metadata, expired transients, unused options from deleted plugins, orphaned postmeta entries, and thousands of cron tasks that never execute properly.
Most users try to fix the problem with database plugins. These tools are useful for basic cleanup, but they cannot solve deeper structural issues such as bloated autoloaded data or inefficient indexes. Manual MySQL optimization gives you real control and unlocks performance gains that plugins cannot reach.
Database optimization impacts TTFB, backend speed, WooCommerce performance, CPU usage, and overall server load. With proper manual tuning, your website becomes faster, more stable, and far more scalable.
If you want to combine database tuning with full-stack performance improvements, check our WordPress Speed Optimization Service.
Understanding the Core WordPress Tables
To optimize the database effectively, you need to understand what each table does and why it may become bloated.
wp_options
Stores global WordPress settings, plugin configurations, and cached data. The most critical column is автозагрузка, which loads on every single page request. If this table contains megabytes of unnecessary autoloaded entries, your TTFB will suffer.
wp_postmeta
Contains metadata for posts, pages, and WooCommerce products. It often holds unused or orphaned data from deleted posts and revisions.
wp_cron
Stores the entire WordPress scheduled task system. When plugins repeatedly register events, this table can grow out of control.
Transients
Temporary cached values stored inside wp_options. They often expire without being removed automatically.
A healthy database keeps these tables small, indexed, and free from expired or orphaned content.
1. Cleaning wp_options and Reducing Autoload Size
The wp_options table has the biggest impact on performance. The goal is to reduce the autoloaded data to under 1 MB.
Check the overall state of the table:
Find the heaviest autoloaded entries:
You will often see leftover data from unused plugins, enormous tracking logs, or WooCommerce session data that should have expired but didn’t.
Remove unnecessary options:
If a plugin was uninstalled incorrectly, many unused options may remain. Reducing autoloaded data from 5–10 MB to under 1 MB can improve server response time dramatically.
2. Cleaning wp_postmeta and Removing Orphaned Metadata
The wp_postmeta table is usually the largest in any WordPress installation, especially WooCommerce sites. Over time, it collects metadata related to posts that no longer exist.
Identify orphaned postmeta entries:
Delete them safely:
Remove empty or unused metadata:
After cleaning, queries involving postmeta (especially WooCommerce product pages) become significantly faster.
3. Removing Expired and Unused Transients
Transients store temporary cached information for plugins and theme functionality. WordPress should delete expired transients automatically, but in reality they often remain stuck inside the wp_options table.
Remove all transients:
Remove only expired transients:
Some sites accumulate tens of thousands of expired transients, dramatically slowing database lookups.
4. Cleaning wp_cron and Reducing Scheduled Task Overload
The internal wp-cron system frequently becomes overloaded with duplicated or stuck tasks. This can slow down both frontend performance and the WordPress admin area.
Check cron size:
If the cron entry is unusually large, reset it:
WordPress will automatically recreate the cron entry on the next scheduled event.
For improved reliability, disable the built-in cron and use a real system cron job.
Add to wp-config.php:
Then set up a server-level cron to call:
https://yourdomain.com/wp-cron.php?doing_wp_cron
This reduces CPU spikes and makes scheduling predictable.
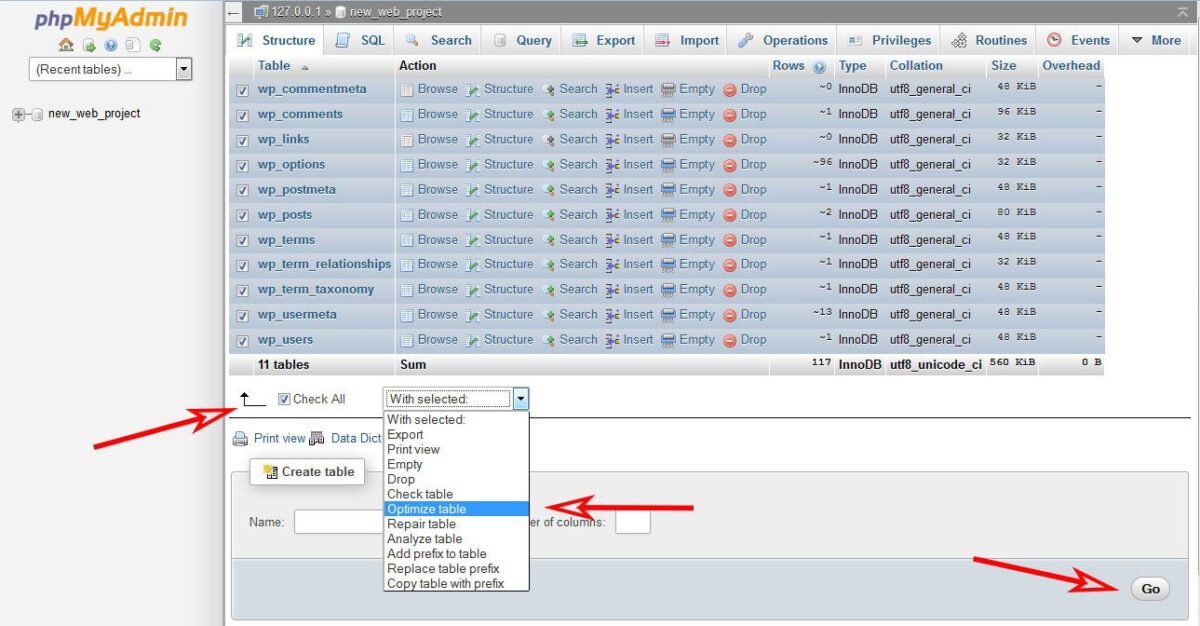
5. Optimizing Tables and Adding Useful Indexes
After cleaning the database, run physical table optimization to defragment storage and improve performance:
For large postmeta tables, adding an index can significantly boost query performance:
This helps especially when using WooCommerce or advanced custom fields.
6. Automating the Process with WP-CLI
For developers and agencies, automation saves hours of maintenance time.
Useful WP-CLI commands:
Schedule these via a cron job to run weekly or monthly for continuous optimization.
Real Case Study: SpeedWP Pro Optimization Results
A WooCommerce client approached us with severe performance issues:
Database size: 380 MB
Autoloaded data: 6.2 MB
TTFB: 700–900 ms
Admin dashboard extremely slow
After manual optimization:
Removed 140,000 expired transients
Reduced autoload from 6.2 MB to 0.9 MB
Deleted 80,000 orphaned postmeta entries
Optimized all major tables
Results:
TTFB improved by 42%
Admin load time dropped from 3.8 seconds to 1.6 seconds
MySQL CPU usage decreased by 35%
WooCommerce product edits became significantly faster
This demonstrates how manual MySQL tuning can achieve improvements that plugins cannot match.
WordPress database optimization goes far beyond clicking a single “clean database” button. Real performance gains come from understanding how MySQL stores data, identifying what is slowing the site down, and removing it safely and strategically.
By controlling autoloaded data, clearing orphaned metadata, managing cron tasks properly, and using SQL-level optimization, you ensure that your WordPress installation remains lean, fast, and scalable — even as it grows.
If you’d like a professional database audit tailored to your site, request a Free Performance Audit here:
https://speedwppro.com/free-audit